India has emerged as a global hub for startup innovation and entrepreneurship. The Indian startup ecosystem has grown exponentially over the past decade, with funding increasing from $1.6 billion in 2016 to $14.5 billion in 2021.
However, many promising entrepreneurs still face significant challenges in raising funds to turn their dreams into reality. This comprehensive guide explores practical strategies and diverse funding options to help aspiring founders in India secure the capital they need to build sustainable, scalable, and impactful businesses.
Introduction
The entrepreneurial bug has well and truly bitten India. Inspiring success stories like Ola, Paytm, and Freshworks have captured national imagination and spawned thousands of promising startups across sectors like fintech, healthtech, edtech, e-commerce, and more.
However, the journey from an innovative business idea to building a unicorn startup is often complex and capital-intensive. Most founders starting out lack the financial resources or networks to self-fund their ambitious ventures. Raising external funding is thus crucial but easier said than done.
“Investors invest in people, not just ideas.” – Marco Giugni, CEO and Co-Founder, Hole19
This guide serves as a comprehensive playbook to help aspiring Indian entrepreneurs navigate the dynamic world of startup fundraising, clarifying the diverse options available and offering actionable strategies tailored to different business stages.
We cover crucial topics like:
- Evaluating funding needs and timing
- Crafting investor-ready business plans and pitching
- Understanding emerging funding trends in India
- Building networks and managing investor relationships
So whether you are just starting out with a seed of an idea or building upon early traction, read on to explore practical tips and insights to turn your entrepreneurial dreams into reality!
The Funding Landscape for Indian Startups
Let us start by understanding the macro fundraising landscape for startups in India and how it has rapidly evolved in recent years.
The Explosive Growth of Indian Startup Ecosystem
The Indian startup ecosystem has witnessed exponential growth since 2016, with yearly funding growing over 3x from $4 billion to $14.5 billion in 2021. The number of startups recognized by the government also increased from 726 in 2016 to over 72,000 in 2022.
Several structural factors are powering this entrepreneurship wave:
- Large domestic market with rising internet and smartphone penetration
- Policy support via initiatives like Startup India and Make in India
- Increased capital availability from VCs, angel investors and government funds
- Emergence of unicorns like Paytm, Ola, and Lenskart that inspire new startups
- Global investor interest in backing Indian tech innovation
Consequently, India now ranks 3rd globally in terms of startup ecosystem value, trailing only the US and China.
This vibrant landscape offers unprecedented opportunities for founders across sectors, provided they can secure the necessary startup funding.
Key Funding Stages and Investor Expectations
Like any journey, startups progress through different growth stages, each requiring different funding strategies from bootstrapping to venture capital.
1. Bootstrapped/Pre-Seed Stage
The earliest stage with no external funding is bootstrapping, where founders self-finance through personal savings, loans or grants. This helps validate initial product-market fit.
Typical funding required: < $250k
2. Early Stage
This stage focuses on market validation and product development. Angel investors provide the first institutional capital.
Includes:
- Seed funding: Early product development
- Pre-Series A: Beta product, initial users
Typical funding required: $250k – $2 million
3. Growth Stage
The startup finds growing product-market fit and scales infrastructure, team and customer acquisition efforts.
Includes rounds like:
- Series A: Scaling product with proven adoption
- Series B,C,D etc: Rapid customer and revenue growth
Typical funding required: $2 million – $15 million+
4. Late Stage
The focus is on expansion into new markets and geographies. Typical investors include private equity firms, investment banks and secondary buyers.
- Pre-IPO stage: Preparing for eventual public listing to raise large amounts of capital
Typical funding required: $15 million+
Understanding these startup stages is crucial because investors evaluate funding eligibility and set their return expectations accordingly. For instance, seed stage investors bet on the team and product’s early traction to provide small capital, while Series A investors look for a proven business model and return potential to provide higher investments.
As a founder, being aware of your startup’s stage will allow you to target the most relevant investors and tailor your fundraising messaging appropriately.
“Have a fundraising strategy tailored to your startup’s stage” – Anil Joshi, Managing Partner, Unicorn India Ventures
Crafting an Investor-Ready Business Plan
Let’s start with an invaluable tool in every founder’s funding arsenal – the business plan.
A solid plan acts as your startup’s resume – succinctly capturing your vision and potential to both communicate with investors and execute effectively.
While an early-stage plan summary might suffice initially, a detailed 10-15 page document is essential once external funding is sought, to demonstrate well-rounded thinking and planning.
Here are the key elements your business plan must cover:
1. Executive Summary
As the name suggests, this section offers a broad overview of key details:
- Business concept: Your product/service, unique value proposition and target customers
- Market opportunity: Addressable market size, consumer demand trends
- Competition: Key players in the space and your differentiation
- Management team: Founders’ expertise and credentials
- Funds required: Capital needed to achieve clearly defined business milestones
- Investor returns: Revenue projections, exit strategy and ROI
Keeping this crisp and compelling sets the tone for your entire plan.
2. Products and Services
Enthusiastically describe what your startup does and highlight:
- Product details: Features, dependencies, development roadmap
- Competitive advantage: Points of differentiation from rivals
- USP: Benefits offered to target customers and how you add value
- IP protection: Patents, trademarks, trade-secrets etc. that secure your innovations
3. Market Analysis
Demonstrate a strong grasp of your industry drivers and trends by covering:
- Target customer segments – Buyer personas, demographics, psychographics
- Total addressable market – Current and expected market size
- Competitor overview – Direct and indirect alternatives for customers
- Market trends and drivers – Macro forces shaping industry growth
- Product fit – Customer need gaps fulfilled by your offerings
Back market claims with relevant research data, citations and future projections.
4. Go-to-Market Strategy
Detail a concrete expansion roadmap across 4 key fronts:
1. Product: R&D, enhancements
2. Team: Hires, partnerships
3. Marketing: Campaigns, channels
4. Revenue: Monetization, projections
Supporting visualizations like a personnel plan, sales forecast graph and marketing calendar help build credibility.
5. Traction
Demonstrable traction conveys ability to execute and often accelerates funding interest. Relevant metrics could include:
- Active users and customer testimonials
- Revenue and downloads
- App installs and engagement
- Trials deployed or leads generated
Highlight key achievements, endorsements and growth rates.
6. Management Team
A startup’s team serves as the face of execution capability and potential. Capture founder credentials like:
- Domain experience: Specific expertise and achievements
- Leadership experience: Past teams or ventures handled
- Educational background: Relevant qualifications
- Personal attributes: Skills, passion and motivation
Compliment withdetails of strategic advisors and potential management hires.
7. Financial Plan
No business plan is complete without addressing the numbers. Furnish details across 3 key fronts:
1. Fund utilization: Breakdown of capital usage towards product development, hiring, marketing etc.
2. Revenue forecasts: Detailed projections of key revenue and cost streams, supported by明 assumptions. Highlight expected growth rates.
3. Investor returns: Specify preferred terms like expected valuation, projected exit timeline, nature of investor exit (IPO, acquisition), and targeted ROI multiples. Share data backing projections.
Take time to thoroughly research input costs, price points, adoption lifecycles and revenue models in your domain.
8. Appendix
Close by furnishing any additional info relevant to conveying your idea’s merit like:
- Product wireframes or prototypes
- Market research reports
- Partner, client or user letters of intent
- Team member resumes
- Press coverage secured
Thoughtfully incorporating each element described above demonstrates thorough business planning and readiness that can instantly intrigue potential investors. Keep the document designer friendly by balancing text, data and visualizations for easy skimming and recall.
While crafting your plan, also actively seek feedback from mentors in your ecosystem like SIDBI, NABARD advisors or small business development cells in your state. Their insights can spotlight aspects needing fine-tuning.
Exploring the Best Funding Sources for Your Business Stage
With a polished business plan ready, let’s examine suitable funding sources to target at different stages of your startup journey.
I. Bootstrapping – The Cornerstone for Early Capital
The early days of turning your idea into reality requires just a small capital push. Rather than rushing to external funding sources, bootstrapping is often the ideal financing mechanism at this stage.
What is Bootstrapping?
Bootstrapping essentially means relying on your personal finances and other internally generated sources to self-fund your venture initially. This helps kickstart operations, establish proof-of-concepts, and even validate market demand on a small scale.
Common bootstrapping avenues include:
Personal savings – tap into savings accounts, fixed deposits
Credit cards – use cards with attractive promotional 0% interest periods
Loans – avail secured loans against property
Income from day job – fund startup alongside full-time employment
Family and friends – request small investments from trusted well-wishers
Crowdsourcing – pool small contributions from a large group of interested backers instead of select institutional investors.
Additionally, once launched, the startup can fund itself by reinvesting revenues, profits, and any surpluses back into the business.
Advantages of Bootstrapping
Self-financing your early development offers 3 key advantages:
Full ownership and control – avoids prematurely diluting equity or decision rights
Business fundamentals focus – places emphasis on thrift, mindfulness of expenses and developing lean operations
Runway for proof-of-concept – allows establishing prototype, securing early adopters to build next fundraising pitch
Globally, founders of Apple, Microsoft, Amazon and Dell bootstraped their way to validation before raising external funding for growth.
When Does Bootstrapping Make Sense?
More founder-driven startups are sustainably bootstrapping longer before raising institutional growth capital. However, self-funding suits certain startup types more than others.
Factors supporting successful bootstrapping include:
- Low initial capital needs – Minimum viable product development has smaller upfront costs
- Potential for quicker revenues – Revenue starts materializing earlier to fund growth
- Focus on profitability – Positive unit margins/low customer acquisition costs
- Modular scalability– Capacity can be added in smaller increments
- Persistent founder effort – Hustling talent and personal savings funds growth
Types of startups compatible for bootstrapping include:
- Cost-effective software products
- Tech consulting services feeding implementation revenues
- Consumer e-commerce with dropshipping preorder models
- Marketplaces earning transaction fees
- Digital marketing agencies
“The leanness and focus instilled through bootstrapping helps startups better attract funding later.” – Ankur Mittal, Co-founder, Inflosion
Bootstrapping is thus ideal for early ideation and product-market validation when capital requirements are smaller. The path gets trickier once large teams, inventory, infrastructure or marketing investments become necessary for scaling.
Transitioning to External Funding
Once rapid expansion needs outgrow bootstrapping bandwidth, carefully determine optimal timing and funding mix to dilute ownership minimally.
Factors indicating readiness for external capital include:
- Traction metrics demonstrating solid product-market fit
- Distribution partnerships that can ease scaling
- Changing market dynamics requiring rapid responses
- Clear visibility into funding utilization and associated ROI
Common funding mix options at this stage:
- Angel/seed investments – getbetween $250k to $2 million
- Crowdfunding – raise smaller amounts from crowds vs institutions
- Bank loans – avail collateralized credit lines for working capital
By organically bootstrapping early operations, you can gain much sharper clarity into realistic capital requirements, own more equity entering external rounds and command better valuation and leverage when you do raise funding.
Bootstrapping combined with wise external financing thus gives your startup the best chance of sustained success.
II. Government Sponsored Startup Funding Schemes
Beyond self-funding, the Government offers over 58 startup schemes spanning loans, grants and incentives to promote entrepreneurship across sectors, demographics and stages.
These schemes ease capital access by addressing common startup roadblocks like high risk, lack of sizable collateral and revenue track records.
Let us explore some popular options:
1. Startup India Seed Fund Scheme
Overview: Central government initiative providing accessible seed funding
Funding offered: Up to Rs 20 crore debt funding
Benefits: Flexible terms, no collateral, equity-free
Eligibility: Innovative Indian startups under 7 years old, past government recognition ideal
Application: Online via startupindia.gov.in portal
2. Credit Guarantee Fund for Startups
Overview: Collateral-free debt facility for startups via SIDBI
Benefits: Government backed funding without asset security requirements
Maximum funding: Rs 2 crore for product startups, Rs 7.5 crore for services startups
Interest rates: As low as 9-10% p.a.
Eligibility: Revenue up to Rs 25 lakh, past incubation ideal
Application: Via startupindia.gov.in portal
3. AIF Fund of Funds Scheme
Overview: Government sponsored VC fund contribution
Benefits: Stimulates institutional investor interest in startups
Funding corpus: Rs 10,000 crore reserves
Eligibility: SEBI registered Alternative Investment Funds (AIFs)
Application: Directly contact target AIFs under this scheme
Such initiatives make seed and early-stage capital access cheaper, convenient and risk-tolerant – appealing to early-stage entrepreneurs.
Finding Relevant Schemes
Over 100 state and central government schemes exist for MSMEs and startups. Identify options suiting your:
Business stage – seed funds for early innovation vs. loan guarantees supporting prototyping/scaling
Location – state based assistance programs like Kerala Startup Mission
Bankability – collateralized bank loans vs. unsecured grants and guarantees
Sector – fintech, edtech, manufacturing etc. specific incentives
Team demographics – special incentives for women founders, rural entrepreneurs etc.
Sources to discover most relevant schemes:
- Government portals like startupindia.gov.in and msme.gov.in
- State industry associations like Telangana State Industry Federation
- NSIC offices in your state
- Bank SME cells and loan managers
- Incubator/accelerator advisors
Leveraging suitable government funding support accelerates gaining strategic maturity and scale.
III. Angel Investing – Accessing Early-Stage Equity
What is Angel Investing?
Angel investors are typically high net worth individuals who provide smaller seed stage capital to promising startups, often investing their own funds vs. those pooled institutionally in venture capital funds.
What do such investors offer apart from capital?
1. Mentorship – leverage their long entrepreneurial experience
2. Connections and visibility – facilitate partnerships and publicity
3. Follow-on funding guidance – onboard later-stage VCs
This makes them appealing even at modest deal sizes.
Angel groups allow individual investors to pool funds and screen deals together. This allows founders to access angel expertise through a single touchpoint while investors can diversity risk.
Common angel deal stats in India:
- Typical investment size: ₹25 lakhs to ₹10 crores
- Equity stake taken: 15-25%
- Investment stage: Early and growth
- Exit horizon: 3-8 years
Finding Relevant Angel Investors
Target investors with strategic relevance, not just deepest pockets by identifying those with:
1. Industry experience – sector-specific insights to evaluate your traction better
2. Strong networks – relationships that could strategically assist your startup
3. Personality fit – work styles and values aligning with yours
4. Post-deal involvement – support potential via connections and mentorship
Ways to find aligned angels:
- Startup events: Conferences and pitch competitions
- LinkedIn: Reach out to founders of similar startups who received
angel funding in the past
- Accelerators/Incubators: Get referrals from their investor networks
- Angel Network Directories: Maps active and accessible investors like AngelList or Let’s Venture
- Founder Referrals: Speak to other entrepreneurs
Building Investor Relationships
Approaching the right investors is crucial but developing lasting relationships further increases funding success.
Follow these tips:
Preparation – Do thorough background research on investors’ sectors, portfolio and check sizes to target most promising matches
Warm Introductions – Leverage accelerators or founder referrals for introducing you instead of cold calls
Concise communication – Introduce your startup concisely and schedule time to discuss further
Responsiveness – Reply promptly to investor queries and concerns
Thought leadership – Share sector insights, not just funding pitches
Rapport – Bond over shared interests and values
Think of investors as partners rather than capital sources and engage consistently from first outreach through due diligence to beyond just funding deals.
This improves financing outcomes and unlocks guidance even from investors who might pass on immediate funding.
IV. Venture Capital – Scaling Growth with Equity Capital
Venture capital firms are institutional investors that raise pooled funds from institutions, endowments, family offices and pension funds to invest in high-potential startups in exchange for equity ownership.
They bet on gaining exponential returns from the outsized growth of few portfolio startups to offset losses from others, allowing for risk-tolerant capital allocation.
VCs provide both financing as well as strategic value adds like global expansion support, executive hiring connects and IPO guidance. However, they have very different risk appetites across startup stages.
Stage-wise Venture Capital Preferences
Venture Capital is segmented by the startup stage they prefer engaging at:
Early-stage VCs: Appetite for riskier startups working on product-market validation to startup revenues (~$1m ARR)
Typical cheque size – $500k-$5 million
Growth-stage VCs: Interested in startups with proven product-market traction rapidly scaling toward $10 million+ revenues
Typical cheque size – $10-30 million
Late-stage VCs: Funding mostly limited to startups preparing for IPO/acquisition exits typically already valued at billions
Typical cheque size – $50+ million
Top India-focused VC firms include Sequoia Capital, Accel Partners, Elevation Capital, Lightspeed Partners, Matrix Partners to name a few.
Attracting Venture Capital Investments
VCs receive thousands of funding requests annually but end up carefully selecting less than 1-2% startups showcasing hardy metrics and differentiation.
How can you grab investor interest?
1. Extraordinary traction: Clear product-market fit visible through meteoric growth and loyal customer base
2. Defensible business: Durable competitive edge making you the preferred industry player
3. Visionary founder: Demonstrable qualities like resilience, adaptiveness and leadership
4. Returns potential: 10X revenue growth in 5 years and $1 billion+ exit potential
5. Scalability: Large addressable market providing vast growth headroom
Essentially, building core business momentum and conveying VC scale criteria convincingly is key to unlocking later stage capital.
Managing the Venture Capital Relationship
Post securing funds, balancing founder-investor dynamics is vital too through:
Strategic utilization of capital towards accelerating growth and agreed KPIs
Proactive progress communication through monthly reports
Responsiveness to suggestions and contacts
Equity-stage based participation rights like investors directing more strategy in later rounds
This ensures continued value-aligned assistance from your investors.
For startups needing significant capital to expand, tactfully leveraging equity funding allows raising growth capital without repayment pressures.
V. Debt Financing – Fuelling Operations with Loans
Venturing down the startup path does not restrict you to just equity issuances. Loans or debt financing allow securing capital which must be later repaid with interest, but does not dilute promoter stakes.
This helps founders retain higher ownership and control.
Debt Financing Avenues
Banks, NBFCs, and specialty lenders offer various debt facilities for startups:
Overdraft funding: Short term working capital need fulfillment through drawing down extra cash from current accounts
Business Term Loans: Medium term capital for operational expenses investment repaid from future cash flows
Machinery/Equipment Loans: Funds for purchasing required infrastructure and machinery
Invoice Discounting: Raising capital against outstanding invoices pending customer payment
Qualifying for Startup Loans
Debt lenders assess eligibility through:
Business viability: Steady cash flows for regular interest and principal repayment
Founder creditworthiness: Personal credit scores indicating responsible borrowing history
Collateral: Hard assets to secure loans against in case of default
Financial performance: Revenue runway, profit trajectory and working capital cycles
Government schemes like CGTMSE and Startup India Loan Scheme ease debt access through collateral-free support.
However, traditional financiers still prefer asset backed facilities from more mature startups.
Added Considerations
If opting for debt, assess preparedness across 3 fronts:
Repayment ability – Will projected cash flows suffice for timely dues clearance?
Affordable interest – Is the effective annual rate viable within budget?
Collateral worth – Can current personal and business assets be pledged?
Debt is advisable once startups demonstrate reliable revenues for servicing additional financing costs. If cash strapped, equity or revenue-linked instruments may suit better.
Non-dilutive financing allows founders to retain higher ownership of thriving startups in exchange for responsible borrowing.
VI. Strategic Investments – Scaling Through Synergistic Partnerships
Beyond direct investment, large corporates often invest as strategic partners. Such partnerships stimulate startup growth while allowing big companies to benefit from emerging innovation.
Strategic corporate investments offer:
Market access: Leverage parent company distribution networks and customer bases
Cross-promotion: Getting marketing support from bigger partner brands
Operational support: Tap into partner resources – technology, infrastructure, teams
Follow-on funding: Potential continued future investment interest
Exit opportunity: Merger and acquisition by parent entity
Additionally, startups gain instant credibility by associating with reputed brand names early on.
Types of Strategic Startup Partnerships
Technology licensing/supply: Startup allows usage of its IP by large firm for licensing fees or branded deployments
Co-branding: Partner with corporates to jointly launch branded offerings as value-added products
Joint go-to-market: Leverage cross-entity sales and channel teams for expanded distribution
R&D partnerships: Collaborate to co-develop new products applying emerging and legacy technologies
For mutual value enhancement, clearly define partnership scope, metrics, exit clauses upfront even within aligned partnerships.
Attracting Strategic Investments
Succeeding sectors like fintech and insuretech see banks and financial services giants partner with startups. Consumer majors also frequently engage startups adding digital capabilities.
Position your startup as an attractive match by conveying:
Unique offerings: Innovative prototypes solving specific business challenges
Commitment: Seriousness via fully developed pitches and product financial projections
Culture: Alignment with would-be partner in work styles and values
Commercial opportunity: Revenue expansion potential for corporate by jointly harnessing strengths
Pursuing corporate partnerships allows startups to scale with established player expertise and distribution might.
Specialized and Non-Dilutive Funding Avenues
The options above cover the seminal launchpads for startup financing across stages. However, India’s funding ecosystem offers specialized platforms that provide alternative benefits.
I. Incubators and Accelerators
Dedicated startup incubators and accelerators offer invaluable funding readiness grooming by providing:
1. Mentorship – Access seasoned founders as guides
2. Fundraising Assistance – Help prepare pitches and make introductions
3. Co-working spaces – Plug into collaborative peer environments
4. Technology access – Leverage shared tools and infrastructure
5. Investor exposure – Get visibility amongst corporate/VC ecosystem partners
6. Seed capital – Some programs directly invest $25-100k
In exchange for mentorship and nominal equity (2-5%), these programs prepare entrepreneurs to attract funding.
Recommended options include Telangana-based T-Hub, IIM Ahmedabad’s CIIE initiative, startup accelerators backed by tech giants like Microsoft and Google along with corporate accelerator programs by financial services giants like ICICI, Yes Bank and Visa.
II. Revenue-Based Financing
Revenue-based Financing (RBF) allows founders to raise funds by sharing future monthly revenues at an agreed percentage rather than equity. As monthly revenues rise, the startup pays higher absolute amounts to investors while retaining ownership.
Benefits of Revenue Based Financing
Flexible repayment – Repayment sizes correlate directly to cash flow health
No collateral – Repaid from operational surpluses sans asset liens
Equity retention – Avoids dilution so founders retain control
This pay-as-you-grow structure helps entrepreneurs secure financing without ownership dilution or repayment overburden through contracted revenue sharing until the drawn amount is fully repaid.
Leading RBF firms in india include GetVantage, Klub, Antler India and Velocity.
India Alternative Investment Funds – Progressing Sectoral Innovation
Beyond commercial VCs, India alternative investment funds (AIFs) offer specialized institutional capital across wider mandates like:
Sector-specific funds: Invest in high-potential segments like saas, fintech, insuretech
Growth-stage focused: Funding reserved for surging growth-stage ventures
Geography centric funds: Specific regions like Bharat-focused VC funds
Women entrepreneur funds: HerVenture Fund, Saha Fund, Ankita Vishwas cater to woman-founded startups
Social impact funds: Target environmental, sustainable agriculture and inclusive space tech startups via Aavishkaar Capital, Omnivore Partners, Caspian Debt etc
AIFs allow customized fundraising for those not fitting the broadest VC mandate but still demonstrating 1864 compelling fundamentals.
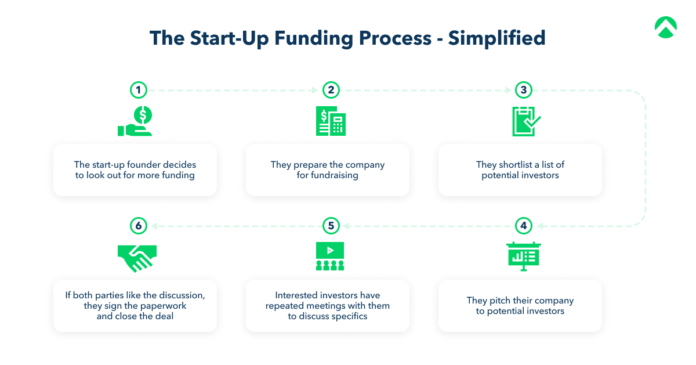
Evaluating and Preparing For Best Funding Fit
Understanding the spectrum of funding instruments at your disposal is crucial. However, securing investor interest involves carefully:
1. Evaluating funding needs and timing – Requirements across product development, hiring, inventory, marketing etc.
2. Researching fitting investor types – Stage, sector and deal preferences
3 Grooming documentation – Business plans, financial models, pitch decks
4 Preparing diligence proofs – KPI dashboards, customer pipeline, prototypes
5. Tailoring communication – Quantify and convey startup maturity, traction and differentiation to influence specific investor categories
6. Responding to queries – Answer investor questions and concerns patiently
7. Relationship building Mindfully engage investors, advisors and other founders
This shapes an investor-centric fundraising strategy tailored to respective appetites and requirements.
Casting the widest net by harnessing technology for promotion beyond physical networks also improves funding outcomes.
I. Leveraging LinkedIn to Attract Investors
As the world’s largest professional network, LinkedIn offers unmatched targeting tools to catch relevant investors’ attention.
Ways to use LinkedIn for fundraising:
Targeted search – Seek Managing Partners, Investment Managers and Investment Associates at VC funds and angels to message
Share startup page – Create an influencer style startup page detailing business model, traction, team etc. to establish thought leadership
Showcase team – Founder profiles should highlight credentials and share career updates about progress
Industry articles – Publish your own or share content demonstrating sectoral insights
Launch targeted ads – Advertise to investors matching right stage, sector and deal size filters
As algorithms closely track engagement, consistent investor community participation expands visibility.
Emerging Trends Reshaping Indian Startup Fundraising
Understanding investor behavior and where capital is likely flowing is crucial to tap into relevant sources. Key trends shaping fundraising include:
I. Fixed Variable Valuations Mainstreaming
Many investors now offer fixed variable valuations to balance risks through:
- Lower seed stage valuation and higher ceiling multiples for follow-on rounds if hitting pre-agreed KPIs
- Attaching round-wise valuations to specific revenue, customer acquisition goals
This gives comfort to investors on returns while allowing founders to command richer subsequent valuations upon promised growth.
II. Revenue-based Financing & Assurance Contracts
Revenue Based Financing structures where founders payback capital as a percentage of monthly revenues are gaining traction given cash flow alignment.
Assurance contracts allow groups to pool funds that get disbursed to entrepreneurs only on fulfilling pre-agreed milestones. This derisks investments in unproven ideas.
III. Emerging Sectors – D2C, Bharat Startups
Backing for promising D2C startups in snack foods, cosmetics, home products etc. are rising given pandemic fueled adoption of digital distribution models.
Investments into startups innovating for Bharat – domestic language internet users, rural communities etc. also looks promising.
IV. ESOP Buybacks & Listings Gaining Prominence
Startups are increasingly launching ESOP buyback schemes mid-fundraise to boost hiring. Indian startups listing on global exchanges signal maturity.
Overcoming Fundraising Challenges with Preparation
Despite upbeat trends, over 60% Indian founders still underscore fundraising challenges including:
Financial literacy gaps – Struggles estimating precise capital and valuation requirements
Low investor confidence – Weak storytelling, market validation and projections
Network gaps – No warm introductions to suitable investors
Term sheet unawareness – Lack of guidance on negotiating investor agreements
Pitch delivery issues – Communication, data interpretation and Q&A performance considerations
However, adequate preparation in above areas helps overcome most challenges.
I. Refining Business Financials and Valuations
Investors commit capital based on return potential. So founders must demonstrate realistic revenue projections, operational metrics and valuations.
Steps to Fortify:
1. Rational funding requirement – Precisely justify needed capital through financial modeling
2. Realistic growth forecasts – Provide sound basis for sales and revenue estimates
3. Margin analysis – Project profit levels at scale based on product/marketing cost drivers
4. Cap table planning – Model dilution at current and future valuation ask
5. Market comps – Benchmark sectoral trends – PE ratios, recent funding rounds etc.
Getting advisors to sense-check is valuable before investor outreach.
II. Demonstrating Traction and KPIs
Investors emphasize market validation metrics proving genuine product-market fit beyond hypotheticals. So showcase traction prominently.
Metrics that inspire confidence:
- Active user or customer growth highlighting product acceptance
- Revenue momentum indicating willingness to pay
- App installs and engagement for digital offerings
- Customer testimonials evidencing satisfaction
- Annual contract value demonstrating customer stickiness
- Partnerships confirming platform value
The more the metrics substantiate and narrate positive user behavior trends, the better.
III. Investor Targeting and Positioning
Even promising startups struggle raising funds by playing to the wrong gallery sending mass approaches instead of targeted pitches tweaked to respective appetites.
Strategizing this by:
1. Researching operations – Analyze portfolios and published investment rationales to identify preferences fit
2. Warm introductions – Leverage founder peers or accelerator connects to access already interested prospects
3. Multi-channel outreach – Email, LinkedIn, networking events, funding platforms
4. Follow-up persistence – Investor meetings seldom convert first time so sustained communication raises chances
5. Addressing concerns – Feedback post any rejections helps strengthen onward targeting
Customizing engagement demonstrates seriousness.
IV. Understanding Term Sheets
Term sheets capture proposed deal terms between investor and founder – amount, round type, liquidation preferences, equity percentages.
As this complex document guides future founder-investor rights and payoffs, study precedents to grasp:
- Different round types – seed, pre-Series A, Series A onwards
- Payment and exit options
- Founder share vesting
- Reserved matters granting investors voting rights
- Distribution of surplus assets during liquidation
Getting advisors to explain implications helps secure favorable terms and capital you need without unequal strings.
V. Pitch Delivery and Messaging
An idea’s best substance can get undermined by sub-par pitching. Investor interactions must cover:
- Hook: Creating an intriguing opening with an insightful statistic or baffling question about status quo inefficiencies
- Problem Positioning: Framing the market need and pain point
- Solution Showcasing: Demonstrating and explaining your product as the relief
- Team Introductions: Detailing capable credentials and commitment
- Traction Highlights: Evidence of initial product acceptance
- Market Sizing: Quantifying total addressable consumers
- Business Model and Metrics: Revenue channels, unit costs and target profitability
- Competition Comparison: Why customers will switch to your offering
- Funding Requirement and Utilization: Precise capital needs and deployment plan
The pitch must compellingly balance startup’s current maturity and projected prosperity. Prepare FAQs addressing concerns around technical viability, adoption reluctance and fulfillment capability.
Airtight responses underpin funding success.
Charting Your Optimal Funding Trail
Wrapping up, attracting investor capital is seminal for founders to unlock exponential value building products and services advancing life and productivity.
India’s funding ecosystem – spanning bootstrapping avenues to strategic corporate partnerships – offers unprecedented options to drive ideas to implementation
Fundraising success ultimately stems from envisioning your startup’s highest potential, crafting strategies realizing that vision and conveying it persuasively to compatible investors through a blend of qualitative storytelling and quantitative profiling.
With adequate self-belief and preparation, India’s ascendant entrepreneurial energy offers wind behind the wings helping startups scale new heights delivering wide-ranging impact – be it inventing sustainable solutions, boosting financial inclusion, advancing industrial efficiency or maximizing human potential.
The future will be shaped by responsible founders who tap into this momentum to create prosperity and progress by unlocking investor confidence and capital strategically at each milestone of their journey.