Introduction
It is a preparation made of dried cells from one or more varieties of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, a fungus employed as a leavening agent in baking. The term “yeast” comes from the Sanskrit “yas” which means “to seethe or boil”.
yeast is a living microorganism that converts starch or sugar into carbon dioxide and alcohol that is the reason wine makers, beer brewers and bread bakers love it. Baker’s yeast is the one we typically use to leaven food items. Baker’s yeast can be active dried yeast (where yeast is alive , but inactive because of a insufficient humidity) and compressed yeast (where the yeast is alive, and is extremely perishable because of it). Brewer’s yeast can be described as a nonleavening yeast used in the brewing of beer. It is also consumed as a food supplement due to its beneficial properties (as as wheat germ) and is not like baker’s yeast that is used to leaven. Brewer’s yeast has a bitter hops taste.
Saccharomyces cerevisiae can be described as the top-fermenting yeast. It is among the most popular kinds of yeast employed in the production of beer, so named because during the process of fermentation it rises to the top of the vessel that is fermenting. Beverages that are top fermenting are known as ales, which is why these yeasts are often known as “ale yeasts”.
Top-fermenting yeasts cannot ferment certain sugars. The resulting beer is more sweet as well as “fruitier”.
Objective
The proposed plan envisages the creating an Baker’s Yeast manufacturing unit for dry and compressed yeast in order to serve the local and international markets of the bakery industry.
The main goal of the document is to aid entrepreneurs in understanding the significance of setting up a the unit that is Baker’s Yeast. This model report can serve as a guideline for entrepreneurs when they begin project as well as providing fundamental technical information to set up an establishment like this.
Raw Material Availability
Sugarcane (molasses) is the principal ingredient in the production of Bakers Yeast. The sugarcane production in the MP region in 2004-05 was 2.14 Lakh MT. The largest production comes from Narsinghpur district. Narsinghpur with the production of 63600 MT in 2004-05.
Suitable Location
The most suitable place to locate this facility is Narsinghpur, Chhindwara, Betul and in a small degree Burhanpur. These areas are suggested considering the productivity and production of the districts. Furthermore, districts are all connected and located in the southern region of the state.
Market Opportunities
In the last few years, yeast extracts have been a major ingredients in savory flavours and also within fermentation processes.
The rise of the Bakers yeast is directly related to the rising trend of fast and processed consumption of food, including bakery products. It is estimated that the European as well as Asian areas produced 51 million tonnes of bakery items worth US $707 million between 2004 and 2005. According to the current worldwide trend China is one of the markets that is most likely to grow for Baker’s yeast since the demand for it is constantly growing due to the increase in the population and the changing demands for bakery products.
Baker’s yeast sales in emerging countries is at new highs due to the increasing demands for processed foods as well as an increase in the production of bakery items to offset the slow pace of growth that ranges from between 1% and 2% in the developed world which are over-saturated. The production of Indian bakery products in 2004-2005 saw an increase of 20%, resulting in approximately 50 lac tonnes of bakery products worth INR around 69 billion. Of the total bakery production bread production was estimated to be around 27 Lac tons, which indicates an increase of 7.5 percent. India’s per capita consumption of bread is 2 kg per year, and when contrasted with other European and emerging nations in Asia it is considerably lower than the most minimal.
According to Government of India trade statistics, the export of Baker’s yeast for the financial year 2006-2007(Apr-Jun) (Apr-Jun) is 329.85 tons, worth INR 28.44 million. The the largest export going towards Sri Lanka followed by Saudi Arabia, Lebanon, Nepal, Mali, Egypt and Iran as imports in the last four years total only 39.18 tons worth INR 2.556 millions. Saf Yeast Co. Pvt. Ltd is a Mumbai located unit that has annual sales less than US $1 million. It is engaged in baking yeast production. Blue Bird India Pvt. Ltd. Mumbai is a Dry yeast distributor in retail packaging for use at home.
The table below outlines the quantity of Baker’s yeast over the past four years:
(Quantity–in Tonnes, Value–in Lakhs
| Years | ||||||
| S. No. | Particulars | 2006–07 (Apr-June) | 2005-06 | 2004-05 | 2003–04 | Total |
| 1 | Export(Q) (V) | 329.85 284.4 | 874.68 707.65 | 19.17 8.38 | 142.94 106.41 | 1366.64 1106.84 |
| 2 | Import (Q) (V) | 16.5 10.67 | 20.5 8.1 | 1.96 4.63 | 0.22 2.16 | 39.18 25.56 |
Is There a Similar Project Report for the Bakery Yeast Production?
When it comes to bakery yeast production, individuals may wonder if there is a similar project report available. While there may be various resources discussing this topic, it’s essential to focus on finding reliable and comprehensive information. If you’re looking for other project reports, such as an automatic curtain opener project report, specific resources or search platforms can aid in your search.
Project description
Applications
Baker’s yeast, like baking powder and baking soda, is used to leaven baked goods (breads, danish pastries, brioche, croissants). The principle use of Baker’s yeast is as an essential bakery ingredient- for causing fermentation in the dough used in making bakery items. This process helps making soft and fluffy bakery items like variety of breads, bread rolls, pizza base, cracker biscuits, sweet breads and burger buns etc.
The useful physiological properties of yeast have led to their use in the field of xylitol [16] biotechnology. Fermentation of sugars by yeast is the oldest and largest application of this technology. Many types of yeasts are used for making many foods: Baker’s yeast in bread production, brewer’s yeast in beer fermentation, yeast in wine fermentation and for production. Yeasts are also one of the most widely used model organisms for genetics and cell biology
Availability of know how and compliances
Baker’s Yeast Technology is available from Central Food Technology Research Institute – CFTRI Mysore.
Capacity of the Project
The capacity of the proposed unit is 38 TPA
Critical Success Factors
Increasing consumption of bread as a staple food rather than just a breakfast item and the industry registering growth rate of around 7.5%, indicate good prospects for Baker’s yeast in the domestic market.
Increasing number of nuclear families and working women in India particularly in urban and semi urban areas and changing food consumption habits and pattern of people, will drive the growth of Bakery industry and in turn the growth of Baker’s yeast demand.
Demand for bakery products is increasing as they are an essential content of many fast food items and people now increasingly prefer convenience products over traditional Indian food items.
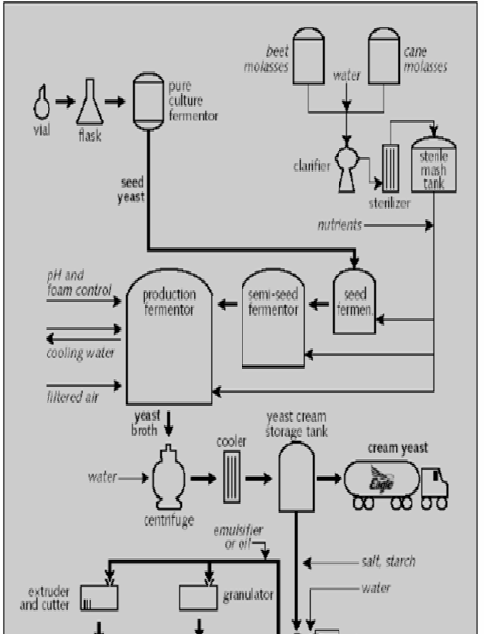
Manufacturing process
Sugarcane or beet molasses is the primary raw material for Baker’s yeast production as it supplies the required sugar and energy with needed nitrogen for the growth of yeast. Cane molasses and beet molasses are the principal carbon sources to promote yeast growth. Molasses contains 45 to 55 weight percent fermentable sugars, in the forms of sucrose, glucose, and fructose.
Raw materials: Concentrated molasses is diluted with water, clarified and heat sterilized before being fed to the yeast.
Fermentation: Bakers yeast begins as a pure culture of the desired strain, which is inoculated from a small vial into a sterile flask of broth. From the flask it is transferred into a larger vessel and then passed through several fermentation stages of increasing volumes.
Processing: The yeast broth from the fermentor at about 5% solids is concentrated in a centrifuge to about 18% solids and washed with water. The cream liquid is this liquid form which is further cooled and passed through a filter that removes water and increases the solids concentration to about 30%. After filtering small amounts of emulsifiers or oils are added to assist in the extrusion, cutting and improving performance of the yeast’s appearance.
The manufacturing process is shown in following diagram:
Project component and cost
Major components of the projects and their costs are described in the table here under:
Land and Building
| Particulars | Unit | Qty | Cost/unit | Total |
| LAND& BUILDING | 8.38 | |||
| Land | SqM | 200 | 250.00 | 0.50 |
| Land Development | ||||
| Land Area | 200 | 500.00 | 1.00 | |
| Building | ||||
| Production Block | ||||
| Buildup Area | SqM | 125 | 5,000.00 | 6.25 |
| Contingencies | 10% | 0.63 | ||
| PLANT&MACHINERY | 2.52 | |||
| Micropulveriser | 1 | 65,000.00 | 0.65 | |
| Sifter | 1 | 15,000.00 | 0.15 | |
| Mixer | 1 | 40,000.00 | 0.40 | |
| Oven | 1 | 80,000.00 | 0.80 | |
| Weighingscale | LS | 1 | 10,000.00 | 0.10 |
| Contingencies | 20% | 0.42 | ||
| MISCELLANEOUSFIXED ASSETS | 0.60 | |||
| Misc Assets | LS | 1 | 50,000 | 0.50 |
| Contingencies | 20% | 0.10 | ||
| PRE-OPERATIVEEXPENSES | 2.12 | |||
| Establishment | 1 | 132,000 | 1.32 | |
| Professional Charges | 1 | – | ||
| SecurityDeposits | 1 | 80,000 | 0.80 | |
| TOTAL | 13.62 |
Plant and Machinery
The total cost of the plant and machinery is Rs. 2.52 Lakhs. The main plant and machinery required for this project are micro pulveriser, sifter, mixer, oven etc.
Building
The main production block will cost around Rs. 6.88 lakhs.
Miscellaneous Assets
A provision of Rs. 60000/- would take care of all the requirements.
Preliminary & Pre-operative Expenses
A provision of Rs. 2.12 lakhs would take care of pre-production expenses like establishment, professional charges, security deposits etc.
Working capital assessment
| ITEMS | Year1 | Year3 | Year5 |
| STOCKOF RAWMATERIAL&PACKING MATERIAL | 0.61 | 0.77 | 0.77 |
| SUNDRYDEBTORS | 4.10 | 5.13 | 5.13 |
| TOTAL | 4.72 | 5.90 | 5.90 |
| MARGIN | 1.18 | 1.47 | 1.47 |
| MPBF | 3.54 | 4.42 | 4.42 |
| INTEREST ON WC | 0.39 | 0.49 | 0.49 |
Means of finance
| EQUITYCAPITAL | 25.00% | 3.70 | ||
| MOFPISUBSIDY | 25% | 50.00 | 25.00% | 3.70 |
| TERM LOAN | ||||
| FINANANCIALINSTITUTIONS | 10.00% | 50.00% | 7.40 | |
| –Payable halfyearlyInstallments | 10 | 0.70 | ||
| TOTAL | 100% | 14.79 |
Cash flow statement
| PARTICULARS | Year1 | Year3 | Year5 | Year7 |
| SOURCES OF FUNDS | ||||
| EQUITY CAPITAL | – | – | – | – |
| SUBSIDY | ||||
| NET PROFIT | 1.18 | 2.88 | 2.27 | 1.64 |
| DEPRECIATION | 0.56 | 0.56 | 0.56 | 0.56 |
| PRELIMINARY EXP.W/O | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 |
| INCREASE IN TERM LOAN | – | – | – | – |
| INCREASE IN BANK BORROWINGS-WC | 3.54 | 0.44 | – | – |
| TOTAL | 5.58 | 4.18 | 3.13 | 2.50 |
Projected balance sheet
| PARTICULARS | Year1 | Year3 | Year5 | Year7 |
| LIABILITIES | ||||
| EQUITYCAPITAL | 3.70 | 3.70 | 3.70 | 3.70 |
| RESERVES&SURPLUS | 3.75 | 6.46 | 9.75 | 12.30 |
| TERM LOAN | 6.70 | 3.90 | 1.10 | – |
| BANKBORROWINGS-WC | 3.54 | 4.42 | 4.42 | 4.42 |
| TOTAL | 17.68 | 18.48 | 18.97 | 20.42 |
Projected profit and loss account
| PARTICULARS | Year1 | Year3 | Year5 | Year7 |
| NET REVENUEREALISATION | 27.36 | 34.20 | 34.20 | 34.20 |
| TOTALEXPENSES | 25.32 | 30.46 | 31.07 | 31.70 |
| GROSS PROFIT | 2.04 | 3.74 | 3.13 | 2.50 |
| DEPRECIATION | 0.56 | 0.56 | 0.56 | 0.56 |
| INTEREST | 1.13 | 0.98 | 0.70 | 0.49 |
| PRELIMINARYEXP.W/O | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 |
| PROFIT BEFORETAX | 0.05 | 1.89 | 1.57 | 1.15 |
| RETAINED PROFIT | 0.05 | 1.89 | 1.57 | 1.15 |
| NETCASH ACCURALS | 0.91 | 2.75 | 2.43 | 2.01 |
| PROFIT &LOSS ACCOUNT | ||||
| OPENINGBALANCE | – | 0.82 | 1.72 | 1.40 |
| CLOSINGBALANCE | 0.05 | 1.89 | 1.57 | 1.15 |
Key indicators
| NETPRESENTVALUE atcurrentInflation(Rs.inlakhs) | 15.11 |
| INTERNALRATEOF RETURN% | 23.50 |
| AVERAGEDSCR | 1.54 |
| BREAKEVEN POINT% | 92.77 |
| PAYBACKPERIOD ( YEARS) | 5.25 |
Manpower Requirement
| PARTICULARS | NO. | |
| SUPERVISORY STAFF | ||
| PRODUCTION SUPERVISORS | 1 | |
| WORKERS | ||
| SKILLED WORKERS | 1 | |
| SEMI-SKILLED LABOUR | 2 | |
| SALESMAN | 3 |
Assumptions
| Project & Financing |
| Contingencies onBuilding 10% Contingencies onEquipment 20% |
| TermLoan50% RateofInterestonTermLoan 10% |
| SubsidyConsidered Subjecttoceiling 25% |
| ExpectedtimeofInstallationMonths 4 |
| Moratorium Months 6 |
| CAPACITY |
| RatedCapacity PerAnnum 80%ofInstalledcapacity TPA38 Number ofOperational Days DAYS300 WorkingHoursPer day Hrs8 |
| CAPACITYUTILIZATION |
| Year I80% Year II90% Year III 100% |
| SALESPRICE |
| W SPrice90000 |
| OTHER EXPENSE |
| Commission 10% Marketing Expenses5% |
| POWER |
| Connected Load HP20 |
| DEPRICIATIONASPERCOMPANY’SACT |
| BUILDING3.34% PLANT& MACHINERY 10.34% MISC.FIXEDASSETS 7.07% LAND &SITEDEVELOPMENT1.63% |
| MAINTENANCE |
| BUILDING 1.00% PLANT& MACHINERY 3.00% MISC.FIXEDASSETS1.50% LAND &SITEDEVELOPMENT1.00% |
The actual cost of projects may deviate on change of any of the assumptions.
